A quick primer
Regulatory and quality compliance across multiple markets can be challenging for medical device manufacturers when scaling globally. This usually requires multiple dedicated resources to support regulatory audit schedules from all the jurisdictions and can cause disruptions to day-to-day operations. If this applies to you, then MDSAP could be a solution.
What is MDSAP?
MDSAP is a global initiative intended to accelerate medical device regulatory harmonization by allowing a single regulatory audit to satisfy the requirements of jurisdictions around the world.
Why MDSAP?
MDSAP was spearheaded by the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF). IMDRF is a voluntary group of medical device regulators from around the world that came together to build on the strong foundational work of the Global Harmonization Task Force on Medical Devices (GHTF). Its primary aim is to accelerate international medical device regulatory harmonization and convergence while protecting public health and safety.
MDSAP was developed to achieve three primary goals:
- Minimize disruptions to medical device manufacturers from multiple regulatory audits while facilitating appropriate regulatory oversight of the manufacturer’s quality management systems.
- Foster the more efficient use of regulatory resources through work sharing and mutual acceptance across multiple countries while respecting the autonomy of each authority.
- Globally advance a greater alignment of regulatory approaches and technical requirements based on international standards and best practices.
MDSAP was launched as a pilot study in 2014 and was fully introduced in 2017 for auditing organizations (AOs) and manufacturers after a successful pilot study and issuance of a Proof of concept report.
The countries that participate in MDSAP
There are five countries currently participating members of MDSAP.
- Therapeutic Goods Administration of Australia (TGA)
- Brazil’s Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA)
- Health Canada
- Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
There are also MDSAP Official Observers:
- European Union (EU)(EMEA)
- United Kingdom’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
- The World Health Organization (WHO) Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs) Programme
And the MDSAP Affiliate Members are:
- Argentina’s National Administration of Drugs, Foods and Medical Devices (ANMAT)
- Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety
- Singapore’s Health Sciences Authority (HSA)
Canada now makes it mandatory to have MDSAP certification for a manufacturer to sell medical devices commercially in Canada.
The other participating countries have some limitations or exceptions in what these regulatory agencies may accept under MDSAP. Some examples
- US FDA will use certification as a substitute for routine inspections.
- In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency will accept MDSAP in lieu of an on-site Japanese Quality Management System audit.
- As affiliate members, Argentina, South Korea, and Singapore can view audit results to assess manufacturers QMS, but their specific requirements have not been added to MDSAP.
- In the EU the use of MDSAP audit reports within the EU legislative framework is possible only where the MDSAP audit covers similar or equivalent MDR/IVDR requirements.
MDSAP audit reports are not applicable to initial QMS audits required for the issue of EU QMS certificates.
The MDSAP Audit Model…. How does MDSAP work?
MDSAP is an auditing approach. The MDSAP audit does not add any additional requirements from ISO 13485 or the Medical Device regulations from the participating countries. Although it’s a single audit program, each participating country adds requirements that are specific to its market.
MDSAP audits are performed by authorized Auditing Organizations (AOs), which are organizations selected by regulatory authorities that meet defined MDSAP criteria. A list of AOs is maintained by the FDA and published on their website.
Similar to the ISO 13485 approach, the manufacturer enters into a contract with an AO to perform MDSAP audits, and there are a number of AOs that can also conduct ISO 13485 audits at the same time. Also, like ISO13485, the audits are conducted on a three year cycle: The initial audit comprises of Stage 1 (documentation and preparedness audit) and then a Stage 2 (implementation) audit in the first year and this is followed by 2 surveillance audits and a re-certification audit in the third year.
MDSAP is a process based approach similar to that of the ISO 13485 process based approach. i.e., the output from one process forms an input into another process.
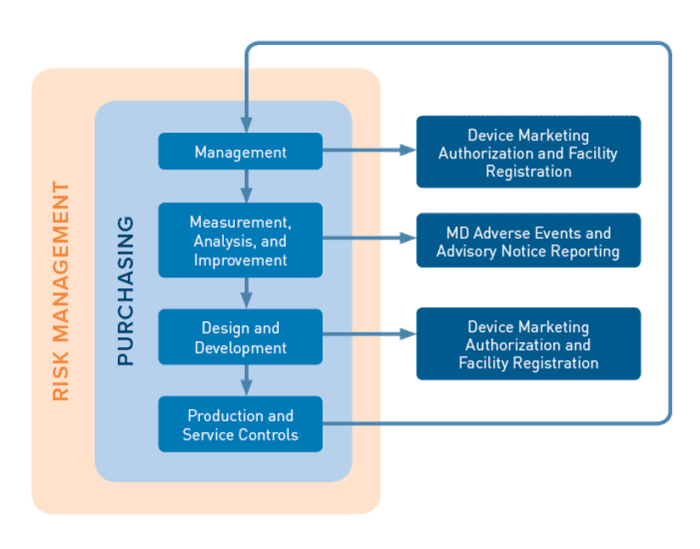
There are 4 primary processes encompassed in the MDSAP audit model
- Management,
- Measurement, Analysis and Improvement,
- Design and Development
- Production and Service Controls
These are supported by the Purchasing process. Device Marketing Authorization and Facility Registration and Medical Device Adverse Events and Advisory Notices Reporting are supporting processes required to fulfil the specific requirements of the participating MDSAP regulatory authorities.
Risk Management impacts are also assessed on all processes to the requirements of ISO 14971.
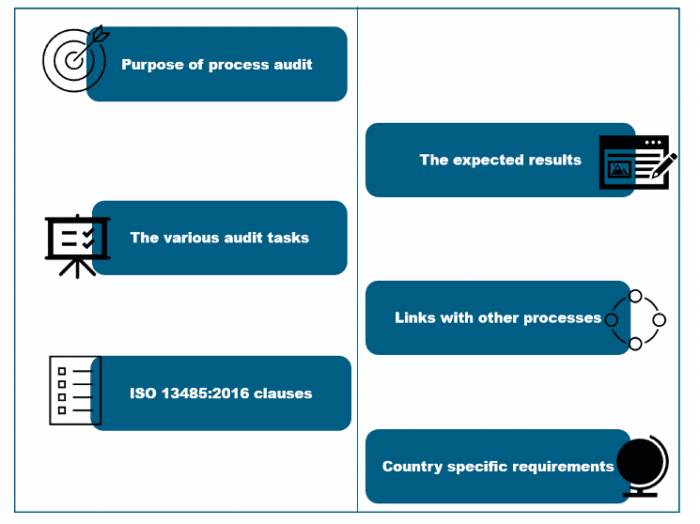
Auditors follow a very structured and logical approach, and the audit moves in a top-down direction with links to the other processes. They follow the requirements of the of the MDSAP audit checklists, and It is expected that they do not diverge from these. Each of the processes clearly defines the audit purpose, the expected results, the relevant ISO 13485:2016 clauses, the specific regulatory requirements of the participating countries, and linkages to other processes. There are defined specific tasks and questions for each process which are the instructions to the auditors for use to verify that the process is complaint to the requirements of ISO 13485:2016 and to the requirements of the country specific regulatory requirements.
It is a very standardized and structured auditing approach that is transparent to all stakeholders including manufacturers. This allows the manufacturer to understand the auditors’ expectations and allow the manufacturer to prepare in advance of the audit.
What are the benefits of MDSAP?
Since one audit covers the regulatory requirements for all participating countries, fewer audits, reduces impact on the organization’s activities and schedules and minimising manufacturing disruptions due to multiple regulatory audits. Less resources are then required to support audits throughout the year.
- Audits are scheduled and planned, allowing manufacturers to prepare effectively.
- There are no surprises. The requirements and audit processes are defined and publicly available in the MDSAP AUDIT APPROACH document.
- One audit enables market entry into five jurisdictions.
- Manufacturers can choose from any one of the approved Auditing Organizations.
How can CAI help?
CAI perform gap assessments, audit preparation, and mock audits for both MDSAP and ISO 13485 with our team of trained certified auditors.
About the Author:

Martina McDonagh, Associate Director of Quality and Compliance
Martina has over 20 years of expertise in the implementation, maintenance, and improvement of Quality Management Systems within the Medical Device and Pharmaceutical Industries. Martina is a Quality and Compliance Leader with extensive experience in developing, leading and managing Quality Assurance teams of Quality Engineers, Quality Specialists, Quality Technicians, and Documentation Control Specialists. Martina is a Qualified Lead Auditor with vast experience of regulatory audits from various global regulatory agencies including FDA, HPRA and ANVISA.